We talk about changing agile mindset for years now, and it’s hard to describe. People who are far from being Agile are often saying “That’s what we are already doing, so what is this buzz about Agile about?” or “This will never work in reality, Agile is only for unicorns.” So let’s see how that agile mindset is changing.
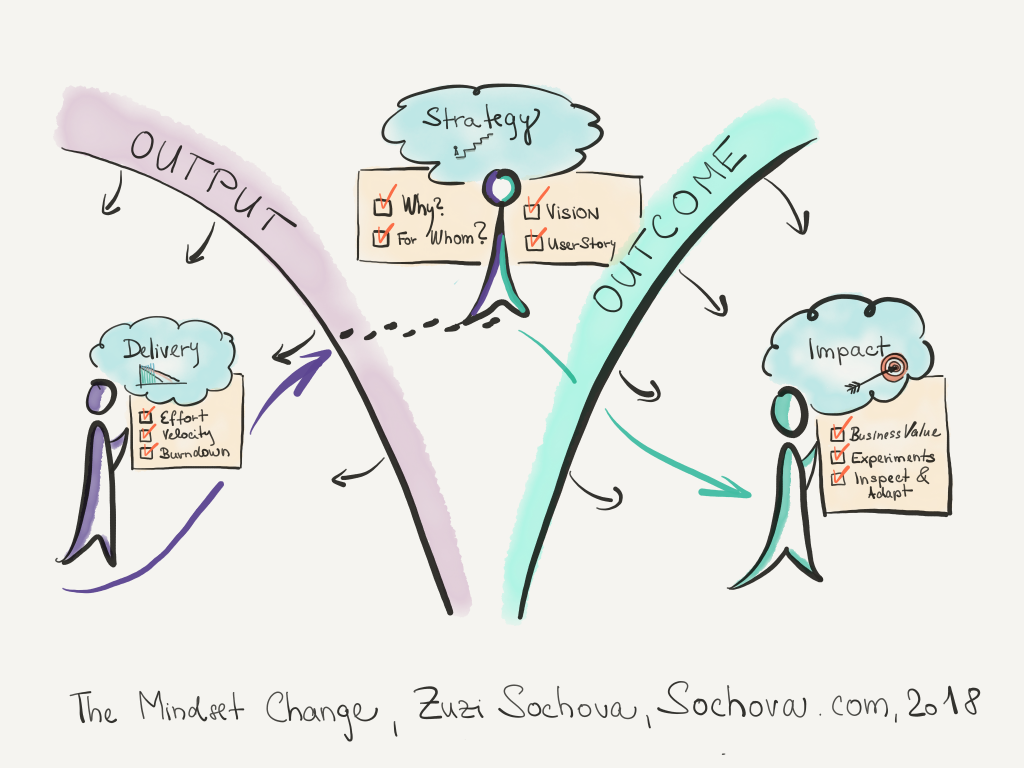
Delivery Focus
At the beginning of the Agile journey, it’s all about output. The delivery is the key. People care about efficiency, measuring velocity, estimating effort and complexity using Story points, T-shirt sizes, drawing Burndown charts. “How can we deliver faster?” is the most common question. People want to measure everything. They still believe the work which needs to be done can be analyzed and planned, so they create mini ‘stories’ aka business requirements with all the details specified, often using acceptance criteria to add even more details and make it even closer to detail specification as they’ve been always creating. They also believe that we only need to follow the plan and deliver everything as described as soon as possible to be successful. Nice and simple world. But that’s not what Agile is about so you can freely forget most of the practices mentioned above. They might be better than some other from pure traditional world, but most of them have nothing to do with being Agile. It’s just ‘fake Agile’. On the other hand, most of the people couldn’t learn how to dance overnight, so a bit of ‘fake Agile’ might be a good step towards the mindset change. To be fair there are some aspect teams need to master at this level, mostly going back to the XP (Extreme Programming) like continuous integration, shared code, TDD, regular refactoring, and pair programming or mob programming. Without those, nothing else will work.
Strategy Focus
The more you apply the agility, and aspects like self-organization to raise empowerment, cross-functionality to be business value driven, and frequent product reviews to be customer-centric, the more your focus turn from delivery to the vision: Why are we doing it? For whom? What makes it different? What is the value? How are we going to change the world? People start to see that delivery is important, but just as a prerequisite. And it’s definitely not about delivering faster (when there is a risk we go to the wrong direction). Instead, it’s about maximizing value, which actually can be achieved by delivering less features than you were used to do before. 80% of the value is only in 20% of functionality, and it’s not distributed linearly. The million-dollar question is how can we know this item brings value. The answer is surprisingly simple: Feedback. You can start with the implementation of Scrum. Short Sprints help teams to focus value delivery through defining Sprint Goals, cross-functional teams enable fast feedback on the value delivered from customers through regular Sprint Reviews, and good Product Owner brings decent business knowledge and creates a relationship with customers so the feedback makes sense. Practices like User Stories and Story Mapping, which are by definition customer-centric and value-driven (if used how they are supposed to be) are useful concepts to start a conversation about the business value. At this stage, people believe that if they have a good vision, and understand the customer well, they are going to be successful. Sounds great, the only weak point is that often that’s not enough in nowadays constantly changing the world.
Impact Focus
Finally, the last stage of the Agile mindset change is acknowledging that we don’t know where the value is, we can’t analyze it, we can’t plan it. All we can do is to iterate and inspect and adapt. This stage is finally where we stop pretending we know where the value is, and start heavily experimenting. Note, that 80% experiments must fail by definition, so you need to run very small tiny reality checks which are expected to be opportunities for learning. Teams learn fast from day to day failures, always looking for better ways, and when every experiment goes as they expected they take is as an indicator of lack of transparency, honesty, and relevant feedback. All over radical transparency is their best friend, empowerment doesn’t stop at the at the team level but goes through the entire organization, and emergent leadership is the key engine to creativity and innovations. The organization is purpose driven and do whatever it takes to achieve it. The delivery at this mindset stage is needed but is quite unimportant. It’s like walking. You would say you need to walk to get somewhere. But if you don’t know where the ‘somewhere’ is, walking no matter how fast only makes you tired. At this stage, it’s not even about a strategy that much as the strategy is emergent and changes depending on the feedback. It’s all about if the outcome we produce created impact. If you know what do you want to achieve, you can measure if it’s happening. The sooner the better. Impact Mapping is a good tool to start. You don’t implement functionality because you know how to implement it, nor because someone believes or say it is a good thing to be done. You do it, to achieve your goal. If you have any evidence that the impact you need to achieve it is happening, you continue. If not, you stop and find another assumption to test. If you think about it, this is a very different way of prioritization, working, and thinking. That’s the real agile mindset. Once you embrace such a way of working, you are truly Agile.