In the world of agile, conflicts are natural part of the team’s journey towards innovation and efficiency. When teams come together to work towards a common goal, they’re bound to have different ideas and opinions. Facilitation is a great tool to help navigate through healthy conflicts. That’s one reason why having a ScrumMaster is always useful. But here I wrote about this many times already. This time I want to introduce a tool that is not that common, but is very useful to have in your ScrumMaster toolbox. Thomas-Kilmann Conflict Mode Instrument (TKI) is a tool, that helps people understand how they handle conflicts and keep your team productive and happy. It identifies five different conflict-handling modes:
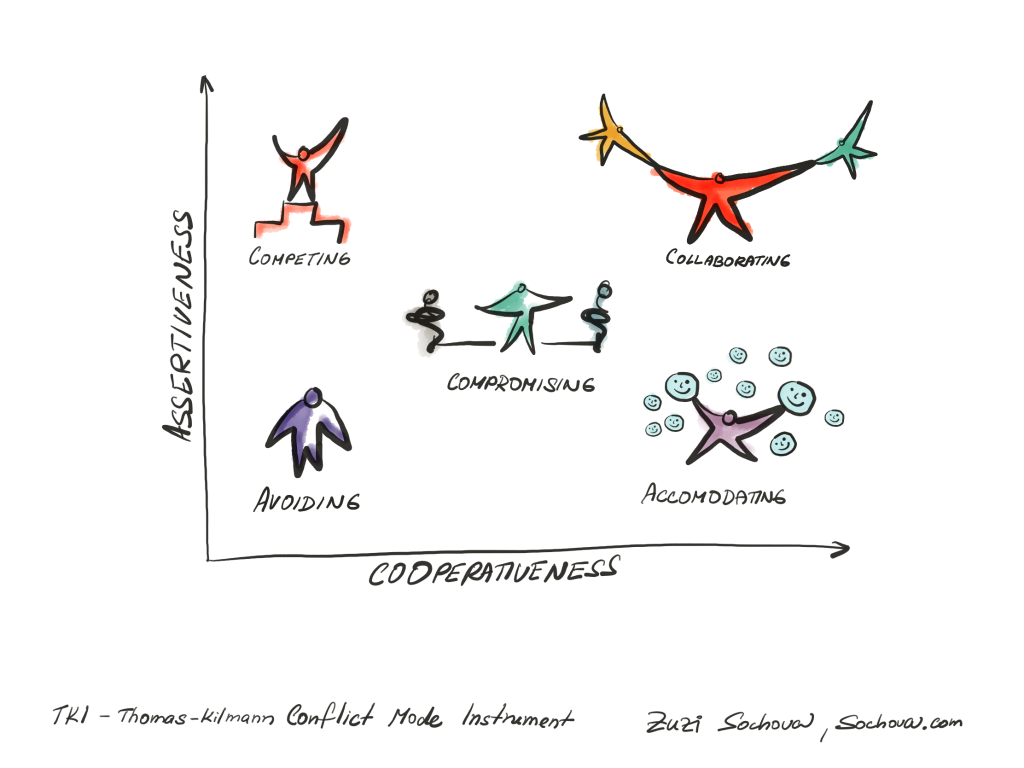
Competing
The Competing mode is in the assertive and uncooperative quadrant. Sometimes, making important decisions without the team’s agreement can damage trust and cause problems. For instance, a Product Owner makes sudden changes without talking to the team, which leads to anger and quality issues. Or a team member pushes their ideas without listening to others, which breaks up the work and creates tension. On the other hand, it’s okay to make quick decisions when you really need to. For example, a Scrum Master can quickly stop a discussion to make sure the team meets a goal, or a developer can say that security is important, even if others are more focused on velocity.
Collaborating
The Collaborating mode is in the assertive and cooperative quadrant. Sometimes, trying to get everyone to agree can slow things down and make teams less efficient. For instance, if you spend too much time brainstorming and trying to please everyone, it can delay decisions and cause a condition called “analysis paralysis.” Or, if you try to include everyone’s opinions, it can expand the scope of the project beyond what’s actually needed. On the other hand, this mode is great for bringing together different perspectives and building consensus when a team works together to make sure technical decisions align with business goals. This can improve product delivery and customer satisfaction, or when developers and the Product Owner collaborate to make sure user stories are clear and prioritized correctly.
Compromising
The Compromising mode is intermediate in both the assertiveness and cooperativeness quadrants. Sometimes, accepting partial solutions can lead to missed opportunities for achieving the best results. For instance, when the team agrees on a solution that partially satisfies everyone but fails to fully meet important technical or business needs, or when sacrificing test coverage to meet a sprint goal, causing later rework and technical debt. On the other hand, it can be useful for achieving temporary settlements like negotiating a minimal viable feature set with stakeholders to meet release deadlines or splitting time between refactoring and delivering new features to balance technical health and value delivery.
Avoiding
The Avoiding mode is in the unassertive and uncooperative quadrant. Sometimes, ignoring recurring problems can make things worse, and it can hurt how well the team works together. For instance, if the team keeps ignoring the same issues, it can lead to technical debt or if a Scrum Master avoids dealing with conflicts, the team can keep getting stuck. But there are times when it’s okay to ignore small problems or when others on the team are better suited to handle certain conflicts. For example, if there’s a non-essential process debate that can wait until the retrospective, or if a developer with deep expertise can handle a minor technical disagreement without involving the whole team.
Accommodating
Finally the Accommodating mode is in the unassertive and cooperative quadrant. Sometimes, trying to please everyone too much can lead to forgetting about important things like technical and delivery needs. For instance, if a developer keeps agreeing to impossible deadlines to keep everyone happy, it can cause burnout, or the team always puts stakeholder demands first, even if it means ignoring technical debt. On the other hand, sometimes it’s good to keep harmony and relationships in the first place. For example, agreeing to small feature requests to build goodwill with stakeholders or when a senior developer lets a junior team member lead a task to gain experience.
Agile teams are all about teamwork, and it’s important for everyone to know how they usually deal with conflicts and how leaning towards different modes can change the team dynamics. For example, if you have a ScrumMaster who is very strong on Avoiding and Accommodating, they might ignore team issues, fail to remove impediments, and compromising agile principles to keep everyone happy for a while. In a nutshell, they’re not really helping teams and organizations change. Great ScrumMasters need to have a balanced profile with high Collaborating to integrate team insights and fostering consensus, and moderate Competing and Compromising to protect the team, keep agile principles, and navigate trade-offs effectively.
In real life, people have a mix of tendencies. For example, imagine you have a Product Owner who is very strong on Collaborating and Accommodating. He will cooperate well with the customers and build great relationships which is awesome but at the same time, they try to make everyone happy and can’t set a clear direction or make a decision when needed.
So how to start? Encourage team members to take the TKI assessment to gain insights into their default conflict styles. Understanding one’s natural tendencies can help individuals consciously choose the most effective approach in various situations.
After that, I usually run a workshop to discuss the five conflict-handling modes and explore scenarios where each mode might be most effective. Using role-playing helps team members practice switching modes and understand the perspectives of others.
Great Scrum Masters are a great help. They are good at recognizing conflict modes and are able to help teams find the most constructive way to deal with conflicts. They coach individuals to reflect on their tendencies and help them to create a better balance. They’re the ones who make sure everyone feels safe to share their thoughts, and they step in when things start to get too heated.