In most of the surveys about barriers of agility in organizations, you learn that the top three places are culture, structure, and leadership. There is no surprise. Organizations were designed for a different world where you can analyze the situation, plan what you are going to do, cascade the goals through the organization, and deliver it accordingly with minimum change requests, simply for the predictable world. The problem is that in the last decades the world has become less predictable and changes were more frequent, the VUCA challenges overtake our everyday life reality and the organizations realized they are too slow to respond. Like dinosaurs thousands of years ago. Change is inevitable. Analyzing, planning, and following the plan is not an option anymore.
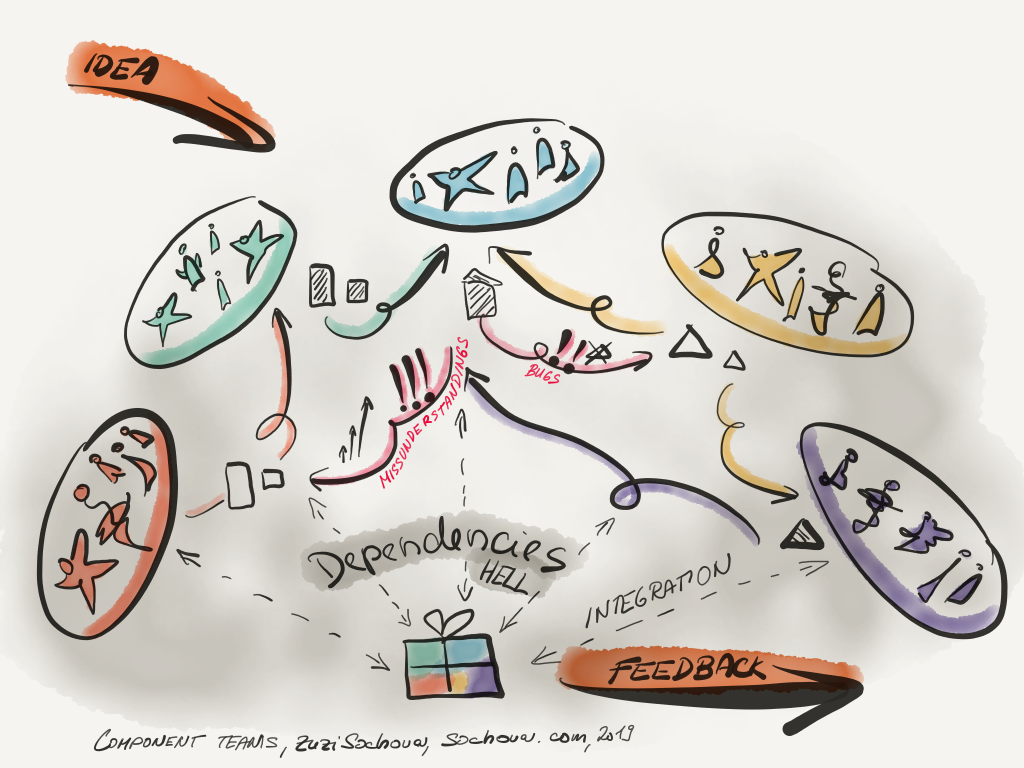
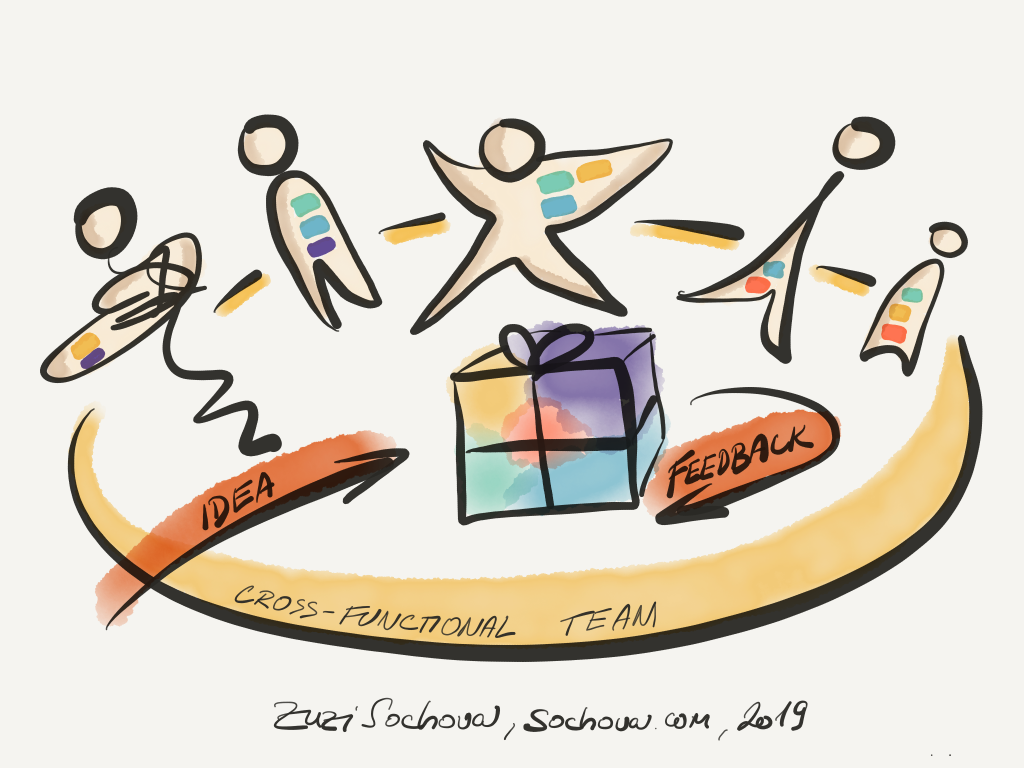
Innovations, creativity, and flexibility are new norm and organizations which can create environments where teams are self-organized, collaborate on maximizing the business value, and co-creating the organizational goals are taking over positions in the Fortune 100 list. Most of the big corporations are still in the cage of the old-world reality. They optimize for speed. But speed is not that important asset anymore as going fast in the wrong direction doesn’t lead anywhere. Instead, we need flexible environments optimized for creativity. Thinking about flexibility, the organizational structure needs to change to allow it. Departments focused on competences or components, not business value, is meaningless. They kill creativity. Hierarchy keeps responsibility by the managers and prevents people from taking ownership and decide themselves. Again, it kills creativity.
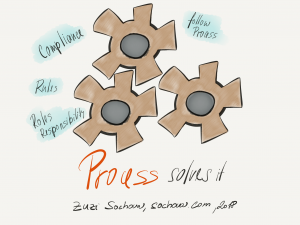
Culturally the traditional organizations are leaning towards competing over collaborating, and controlling over creating. The practices of detailed positions, reward systems, performance reviews, and individual goals and objectives are keeping the organizations in competing and controlling quadrants.
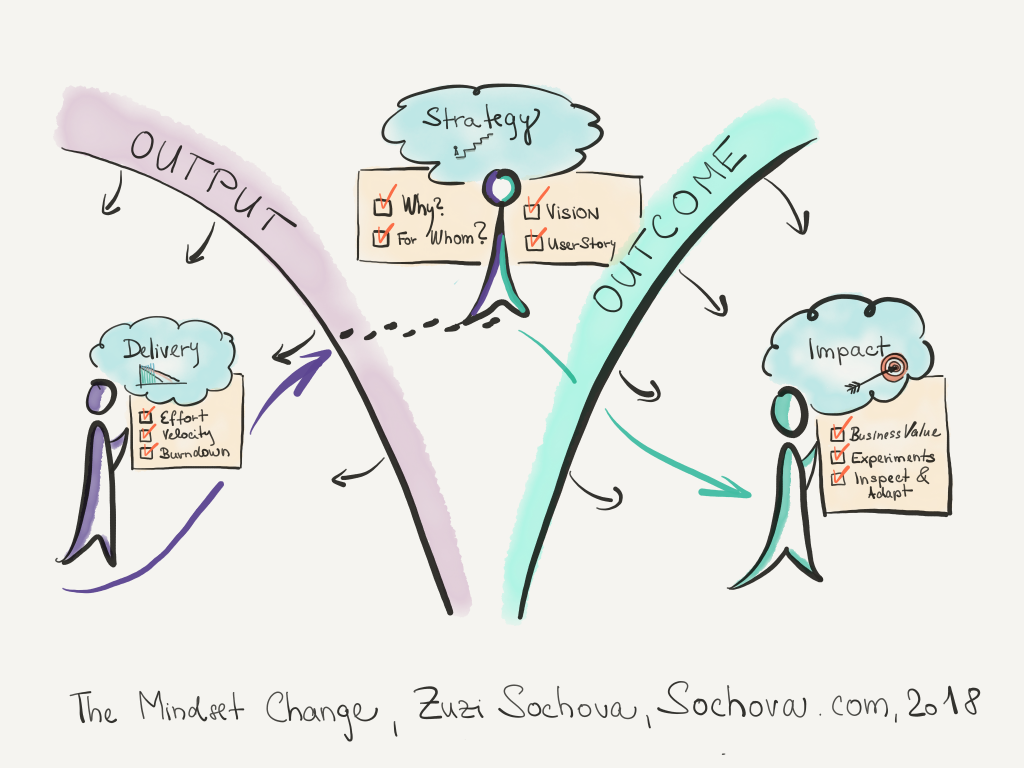
Finally, the leadership needs to change significantly. Traditional organizations were expecting leaders to be Experts or Achievers. Agile organizations need Catalysts. They need leaders who are visionary, purpose-driven, are able to see the business and organizations from different perspectives. They enhance collaboration and are good at building teams and networks. They search for win-win solutions, are good coaches, and helping others to grow. They support running experiments and use failure as learning.
All over we can say that Agile Organization needs different leaders, cultures, and structures. You don’t have to start with changing all of them at once, but sooner or later such change is inevitable. The fewer barriers you give agility on the way, the more likely the frameworks, methods, and practices make a difference and help you to be successful in the VUCA world.